OPERATORS OF INVESTMENT PLATFORMS ARE OBLIGED TO ORGANIZE MEASURES TO AML/CFT
Written by Manuylova NatalyaFrom 01.01.2020, a new entity will appear on the financial market - the operator of the investment platform. In accordance with subparagraph 7) of clause 1 of article 2 of Federal law dated 02.08.2019 No. 259-FL "On attracting investments using investment platforms and on amending certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation" the operator of the investment platform is a business company created in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, carrying out activities to organize investment attraction and included by the Bank of Russia in the register of investment platform operators.
It is worth noting that from 01.01.2020 the amendments to the Federal Law of 07.08.2001 also come into force. No. 115-FL "On combating the legalization (laundering) of proceeds from crime and the financing of terrorism" (hereinafter - Law No. 115-FL), according to which:
1. Operators of investment platforms become the subject of Law No. 115-FL (Supplement to the first part of Article 5 with a new fourth paragraph of the above law);
2. The operators of investment platforms are entrusted with the obligations specified in Article 7 of Law No. 115-FL, including the application of measures to freeze (block) money or other property in accordance with the requirements established by subparagraph 6 of paragraph 1 of Article 7 of Law No. 115- Federal Law.
3. The operators of investment platforms have been granted the rights specified in Article 7 of Law No. 115-FL, in particular:
- simplified identification of investment platform operators with respect to customers in certain cases, namely: when concluding agreements on the provision of investment assistance services involving investment using the investment platform for an amount not exceeding 100,000 rubles, provided that all settlements are carried out exclusively in non-cash form on accounts opened with a Russian credit institution;
- an assignment of the identification procedure to third parties - on the basis of the contract to entrust the credit organization with the identification or simplified identification of the individual customer, as well as the identification of the client’s representative, beneficiary and beneficial owner.
4. The internal control rules of the Investment Platform Operators are developed taking into account the requirements approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in agreement with the authorized body, and approved by the head of the organization.
5. Qualification requirements for special officials responsible for the implementation of internal control rules, targeted internal control rules, as well as requirements for training and education, identification of clients, client representatives (including identification of the sole executive body as a representative of the client), beneficiaries and beneficial owners are determined in accordance with the procedure established by the Bank of Russia.
Please note that non-compliance with the requirements of Law No. 115-FL entails the prosecution of an official and organization on the basis of Article 15.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The consequences of non-compliance with the requirements of the AML/CFT legislation May result in criminal prosecution.
For questions regarding the organization of work on the implementation of Law No. 115-FL and training, write to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. or This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
THE ROUNDTABLE PARTICIPANTS LEARNED ABOUT THE FEATURES OF SMART CONTRACTS
Written by Manuylova NatalyaOn November 5, 2019, a round table was held at the Moscow Chamber of Commerce and Industry on the topic: “Electronic Commerce. Smart contracts. New Opportunities of the Digital Economy ”, which discussed the main problems of legal support of electronic commerce.
At the event, the main trends of the digital economy were presented and the state of legal regulation of this sphere was outlined. According to Suren Vardanyan, Vice President of the Chamber of Commerce and Industry, opening the meeting, the Chamber pays special attention to digitalization issues: digital products are being developed that allow entrepreneurs to receive new services, and the Chamber follows the main economic trends. “We try at all the events that take place within the walls of the MCCI to develop specific proposals, which we then pass on to the authorities and all interested departments,” Vardanyan emphasized.
According to Igor Sudets, Deputy Director of the Digital State Development Department of the Ministry of Digital Development, Telecommunications and Mass Media of the Russian Federation, 17 draft laws are currently being drafted to regulate the main directions of digitalization of the Russian economy. In the near future it is expected that the Government will give instructions on the preparation of about 60 more draft laws. For example, the draft law on digital financial assets has already undergone seven editions, but has not yet been submitted to the State Duma. Now the eighth version of the document is being prepared. The total budget allocation for federal projects related to the implementation of digital technologies is 1634.9 billion rubles. The main national programs being implemented now, according to Igor Sudets, are a training program for the digital economy; digital infrastructure creation; digital technology development; digital security; development of legal regulation and the creation of digital state regulation. As for the latter, as stated by the representative of the Ministry of Communications, the basic principle of digital government is “a person does not need to know which authority he interacts with. He sends a request, and the state executes it. " Moreover, according to the expert, “the state itself should come to us”: after some time, every citizen can receive push notifications about what actions he needs to take: pay taxes, replace a driver’s license, etc.
Artem Dalevich, Vice President of the ICIE, spoke about the implementation of the secure transaction mechanism using escrow accounts on the Business Market platform, developed and implemented by the MCCI
Since lawyers made up a large share of the roundtable audience, one of the main topics of discussion was the legal regulation of electronic commerce. Senior Associate at Rödl & Partner Alexandra Nechaeva spoke about the main risks that accompany the conclusion of contracts in online trading. It was, in particular, about the interpretation of the concept of an offer and the moment of its receipt, as well as about the differences between online and distance trading. The speaker emphasized that there is no definition of electronic commerce in the legislative field, which leads to a rather arbitrary interpretation of the electronic commerce process in judicial practice. In addition, Alexandra Nechaeva said that Russia has not developed approaches to determining the jurisdiction of transactions involving foreign elements. Summing up her speech, the speaker noted that “the problems of determining jurisdiction are now one of the first in matters of the digital economy”.
Svetlana Mochalina, head of the risk management department at L'Occitane, spoke about the legal risks of an international company in the retail industry in Russia. A franchise firm defended its interests by registering trademark rights. This almost completely prevented parallel sales.
The topic of the speech of DDC Ltd Director Ilya Mikheev was smart contracts. Since this is a very promising form of digital agreements, the message caused serious interest from the audience. According to the expert, for the first time a smart contract appeared a long time ago - in 1996. “In principle, a smart contract is a computer code that guarantees the fulfillment of obligations subject to all agreed conditions,” the speaker explained. Another important distinguishing feature of a smart contract is that it must be hosted in a decentralized, trusted environment. Such an environment is guaranteed, in particular, by blockchain technology. Smart contracts are already used, for example, in diamond verification.
The representative of the company-operator of fiscal data OFD.ru Dmitry Pogozhev talked about the currently introduced product labeling system, its advantages and disadvantages.
Summing up the round table, the moderator of the meeting, forensic financial expert Natalya Manuylova noted that "the digital economy is not only cryptocurrency and blockchain." The main purpose of the event was to identify the risks that entrepreneurs face in introducing digital technologies, and to outline ways to minimize them, including using compliance procedures.
The Advisor to the President of the MCCI Marina Evteeva thanked all the speakers and participants for the informative conversation and assured that all the proposals that were voiced would be summarized and brought to the attention of the leadership of the chamber.
The event was supported by the Government of Moscow and the Department of Economic Policy and Development of Moscow...
SEVENTH ACISO CONFERENCE IN MOSCOW (INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SECURITY)
Written by Aleksandr PodobnykhThe seventh conference of ITS Moscow 2019 will be held on November 29 of the current year (at 13:00, Skolkovo Technopark). At the event, a report on the work for 10 years from the Chairman of the Management Board, Viktor Vladimirovich Minin, will be presented.
This year ACISO is celebrating its 10th anniversary. The Association brought together ambitious, successful, talented experts in the field of information security. Also in the program are reports of ACISO Members: Alexander Mishurin, Mikhail Smirnov, Alexander Pershin, Konstantin Samatov, etc.
After which, it is planned to hold the Reporting and Election Conference of ACISO. It is held every two years and is obligatory for visits by all members of ACISO. If a member of the Association does not have the opportunity to attend the event, he draws up a power of attorney for the right to vote.
Source: ACISO.
THE FEDERATION COUNCIL DISCUSSED CURRENT TRENDS IN THE LEGISLATIVE REGULATION OF THE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION OF THE ECONOMY
Written by Manuylova NatalyaThe Chairman of the Federation Council Committee on the Rules and Organization of Parliamentary Activities, Vyacheslav Timchenko, held a round table on the topic "Current Trends in the Legal Regulation of the Digital Transformation of the Economy."
The senator noted that the Federation Council pays great attention to the topic of legal regulation of the digital economy.
“In the upper house of the Russian parliament, an expert advisory body is constantly operating - the Council for the Development of the Digital Economy under the leadership of Deputy Chairman of the Federation Council Andrei Turchak,” said Vyacheslav Timchenko.
According to the parliamentarian, when developing legislative initiatives, it is important to take into account the opinion of the professional and expert communities. “This will create the regulatory framework necessary for the development of breakthrough technologies,” the head of the Federation Council Committee emphasized.
The meeting discussed the legal regulation of the digital economy and services, as well as considered bills that allow the introduction of modern methods in various fields. The participants made suggestions and presented a number of amendments to the documents under discussion.
The discussion was attended by listeners of the program “Legal foundations and legal practices of working with cryptocurrency and blockchain projects” of the G.V. Plekhanov.
During the event, Vyacheslav Timchenko supported a number of initiatives prepared by students in the learning process.
Source: Council of the Federation of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation.
IT BECAME KNOWN ABOUT THE STRANGE TRANSFERS NAVALNY BEFORE LARGE SHARES
Written by Bederov IgorAll investigations and political actions of blogger Alexei Navalny begin immediately after large cash receipts come to his bitcoin wallets, the owner of Internet-Rozysk, Igor Bederov, told the Krasnaya Vesna correspondent on November 6.
He said that his company is developing unique services for the prevention and investigation of crimes intended for law enforcement and security services: “You should start the story with the fact that we are developing the first domestic service designed to trace cryptocurrency transactions - SICP | Security Intelligence Cryptocurrencies Platform."
Igor Bederov recalled that Navalny “uses several cryptocurrency bitcoin wallets to finance his activities,” and spoke about the results of monitoring the status of these wallets.
“What are these wallets? The first wallet 3QzYv * (the wallet number is at the disposal of the publisher) was used in 2691 transactions. In total, 633.28146173 Bitcoins came to this wallet, which is 378 196 391.89 rubles. at today's rate.
The second 3MQTR wallet * (wallet number is at the disposal of the publisher) was used in 666 transactions. A total of 72.80104198 Bitcoins came to this wallet, which is 43,476,863.08 rubles. at today's rate, ”the specialist shared information.
He drew particular attention to the fact that the activities of the opposition are “tied” to the proceeds of his Bitcoin wallets: “During the monitoring of these wallets, we clearly see that all his investigations or political actions take place immediately after receiving a large monetary tranche.”
Igor Bederov noted the difference between such large tranches and the receipt of money from Navalny’s supporters: “Such tranches are very specific and very different from the usual donations from FSC supporters. An ordinary supporter of Navalny can transfer him an amount of 100 rubles. and up to 15 thousand rubles. maximum. And these are direct transactions that go from wallet A to wallet B.
At the same time, large transfers that precede stocks and FSC investigations start at 3 million rubles. And these transactions are far from simple. They mix bitcoins, hide information about their real sender in a heap of parallel transactions."
In conclusion, he emphasized that after the analysis it was possible to establish that the sender of such tranches may be located in the USA: “However, we were able to analyze several chains of such transactions and determine that the probable sender of funds may be located in the United States.”
Note, on October 9, the Ministry of Justice of Russia recognized FSC as a foreign agent.
And in mid-October in 30 headquarters of the headquarters of the Anti-Corruption Fund, the Investigative Committee of the Russian Federation conducted searches. They took place in the framework of the criminal case of money laundering by FSC employees, as well as their receipt of money from abroad. FSC accounts were arrested.
On November 5, the Levada Center released data according to which a third of Russia's residents call criminal cases against the Navalny Fund protection of the country from foreign influence and the fight against money laundering.
Source: Red Spring.
BEYOND REALITY: ACISO CONFERENCE (INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SECURITY)
Written by Aleksandr PodobnykhColleagues, the Association of Chiefs of Information Security Officers (ACISO) invites you to the 8th annual conference of ITS St. Petersburg 2019 (October 10, Prospect Medikov 3-A). Continuing the theme of the year: Beyond reality. The meeting participants will discuss issues of protecting information and the individual as a whole.
Welcoming remarks by the Chairman of the Board of ACISO - Victor Minin, and acquaintance with invited experts will open the event. The program has 3 sections planned, in one of them I will speak, in the light of work on the SICP project: Patrolling blockchains and investment security in the field of cryptocurrency circulation...
In addition, a round table with regulators will be held at the conference, as well as the 2nd version of the manual on the safety of СII (Critical Information Infrastructure) objects of the organization (each participant will get it)!
Source: ACISO.
CLOUDTOKEN - 150X PROFIT OR PYRAMID SCHEME?
Written by Dobryshkin SergeySince the spring of this year, a project called CloudToken is actively developing and promoting the network, positioning itself as "the first wallet in the world that integrates all crypto assets of the blockchain on one platform." Their goal is to provide project participants with a special ecosystem of public savings.
The project supports 7 major cryptocurrencies and stablecoins, 21 referral levels, has a mobile application (wallets in leading marketplaces) and offers its participants a yield of 6 to 12% per month, as well as 150-fold profit (!) For 2019. At the same time, the first participants (top of the pyramid?) Are promised support for the issuance of payment cards.
The project attracts its participants (the number of which, according to some estimates, has already exceeded 800,000 people) with the help of the so-called "network leaders" from around the world. For example, in Russia and neighboring countries, Pavel Chernyshev is engaged in resource promotion.
Information on the project website is presented in English and Chinese, the legal entity Cloud Technology and Investment Pty., LTD is registered in Australia, and the United States is indicated as the geolocation of the site. Currently, 145 countries are involved in the scheme.
The process of making a profit is described on the resource as follows:
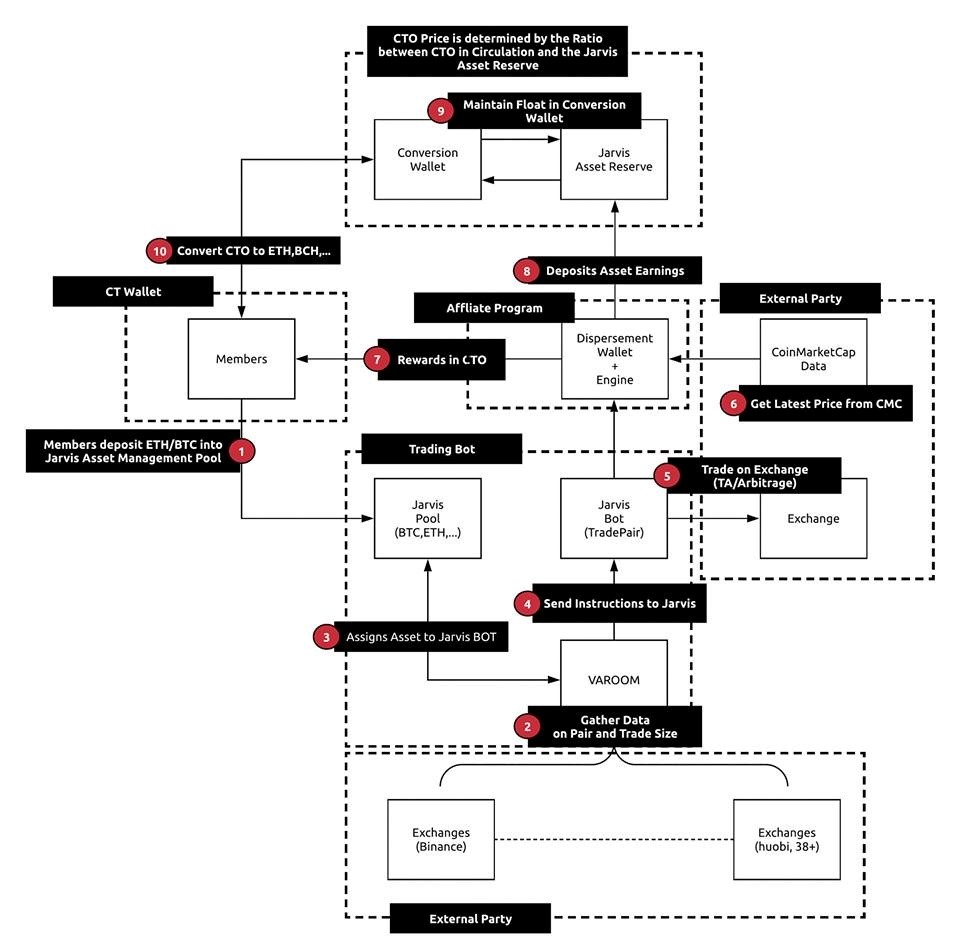
1. Participants send funds to ETH / BTC in the Jarvis bot asset management pool.
2. A tool called Varoom collects data from over 38 cryptocurrency exchanges.
3. Varoom transfers assets to the Jarvis AI BOT.
4. Varoom instructs Jarvis.
5. Jarvis trades on exchanges.
6. Information is collected on the latest prices at CoinMarketCap.com.
7. Members receive rewards in CTO tokens.
8. The rest of the earned funds are transferred to the Jarvis Asset Reserve.
9. Jarvis Asset Reserve supports the rate in the conversion wallet.
10. Participants can convert CTO to ETH, BCH or other cryptocurrency at any time.
The mobile application offered for download is positioned as a cryptocurrency multi-wallet with passive income (while funds can be sent in only one direction), as well as a trading bot (without confirming trading volumes). Nevertheless, judging by the volumes, the funds received from participants (victims?) Are immediately transferred to controlled sites and cold wallets.
According to an investigation conducted by the experts of the cybersecurity resource SICP (sicp.ueba.su), the total amount of funds that have passed through only one wallet currently exceeds 6 billion rubles, and this figure is constantly growing.
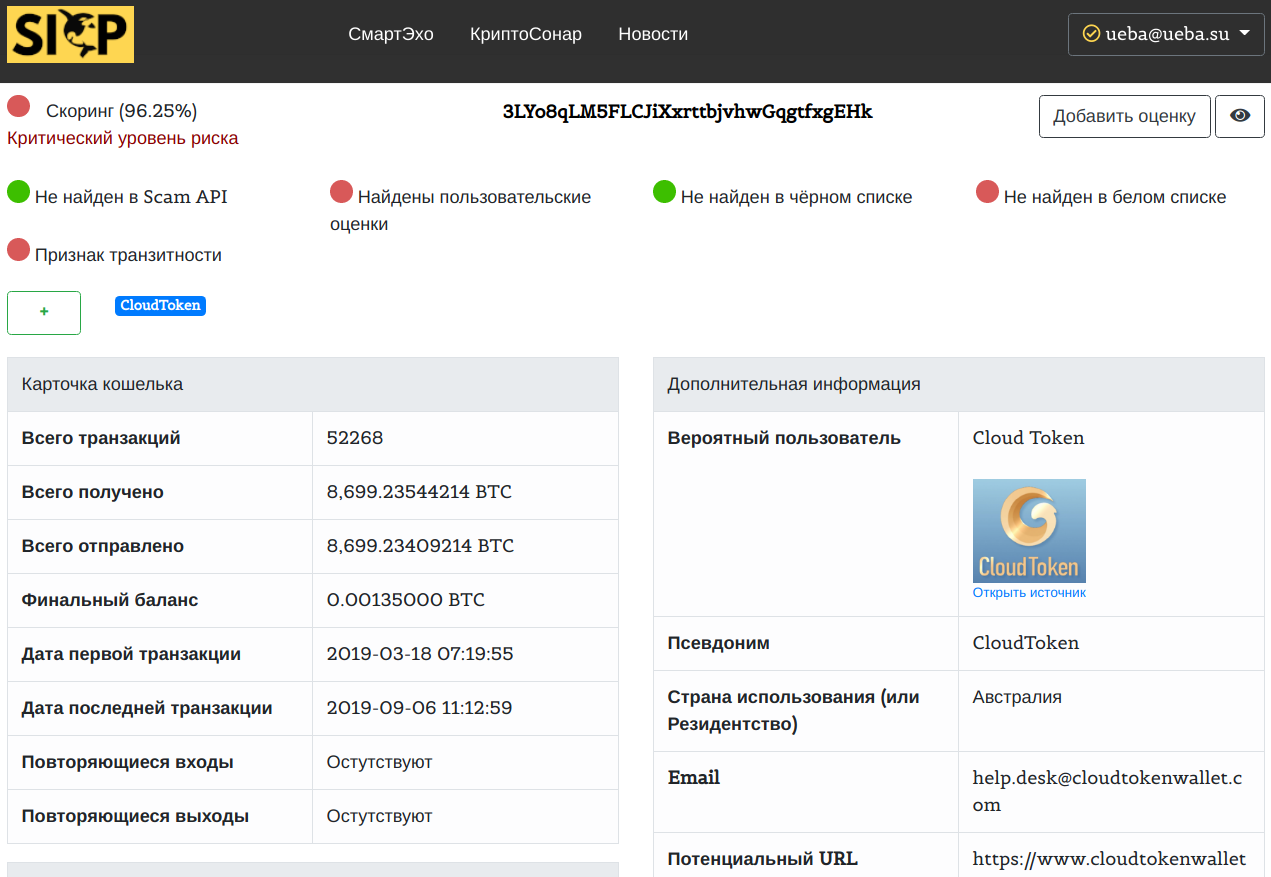
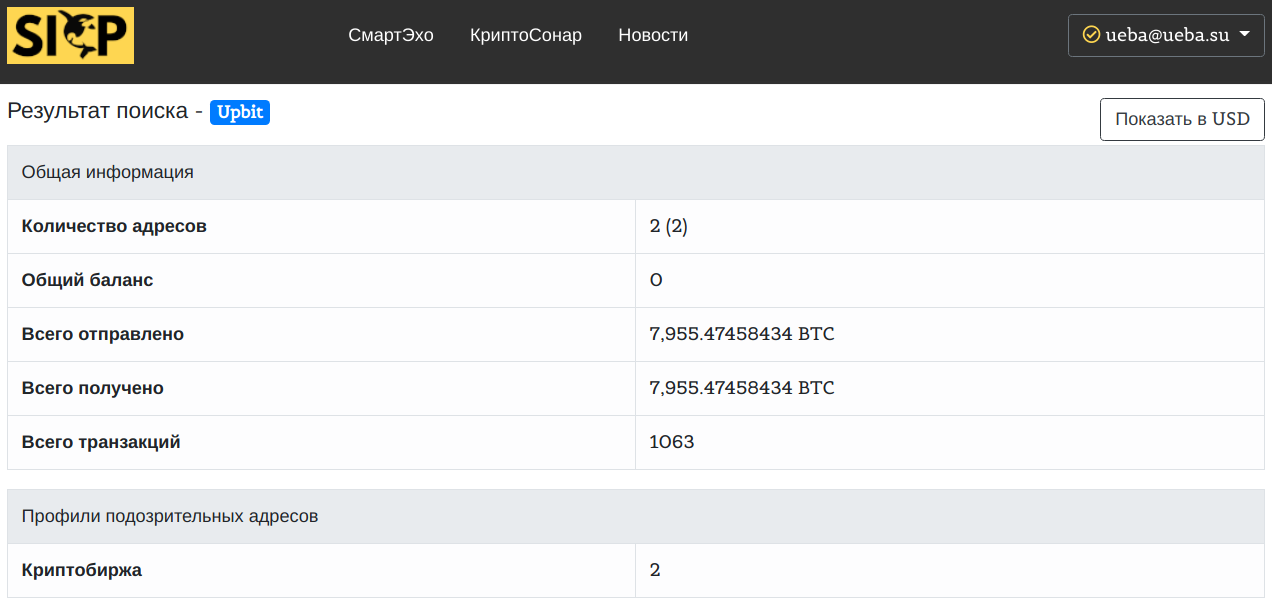
In particular, as a result of the investigation, it was found that all the main assets of the CloudToken project are transferred to the South Korean crypto exchange Upbit, and also are withdrawn through wallets in Thailand (in some cases they are frozen).
Below is some more evidence that the CloudToken project is just another pyramid scheme.
1. Despite the fact that the organizers of the project position it as a “completely decentralized cryptocurrency wallet”, in fact it’s hard to even call it a wallet. In fact, users only get access to the server, where they see their tokens. Judging by the CloudToken tracker on Etherscan, all it can boast of is 4 addresses and 5 transactions, with 99.9999% of the funds held at one address. Thus, buyers give their money, but do not become owners of the coveted tokens.
2. In the promotion of the service involved people who have repeatedly advertised fraudulent schemes.
3. Lack of evidence of trading using the Jarvis bot. Although representatives of the project claim that they generate profit using the Jarvis AI Bot bot, which is used for arbitrage trading on exchanges, there is no evidence of such trading on the resource.
4. Cryptocurrency pyramid based on the Ponzi scheme. Project participants on the referral side need to replenish their account by at least $ 500, after which they will be able to receive commissions for attracted people. In this case, commissions are paid up to level 21. It is unlikely that such a scheme can last long.
5. Lack of use cases. CloudToken does not have application scenarios in the real world, it can only be purchased from developers, and no token exchanges accept. The price of the token is not supported by anything, the demand for it is artificial. The company can change the value of the token at any time.
6. Lack of access to CTO wallet private keys. Users do not receive secret keys from the "wallet", instead they are given a password or PIN code.
7. The promise of high return on investment. Most projects that promise high investment returns actually turn out to be scams, unless the program has official registration and regulation.
8. Invalid information. The White Paper of the project mentions the names of people who have nothing to do with the project.
From the foregoing, we can conclude that CloudToken does not have a secure cryptocurrency wallet, its founders do not trade on the exchange and deceive investors. In addition, the project is advertised by well-known network scammers, and the CloudToken address is involved in the services of doubling bitcoins and the distribution of paid prohibited content.
Source: CryptoRussia.ru
FINMA PUBLISHES STABLE COIN GUIDELINES: EXPERT OPINION
Written by Manuylova NatalyaOn September 11, 2019, the Swiss financial market supervision authority FINMA published an addendum to the ICO manual, which outlined its position on stablecoin1 under the Swiss supervision legislation. Observing the steady growth of stablecoin projects since 2018, in the context of a request from the Libra Association, FINMA in the initial directions provides information on how the Swiss supervisory will apply the relevant rules for the assessment and supervision of stablecoins.
According to FINMA, the supervisor considers stablecoin in accordance with the law on supervision of an existing approach to blockchain-based tokens: the main focus is on the economic nature and purpose of the token (“substance over form”). When making decisions on specific projects, FINMA will “follow the proven principle of“ same risks, same rules ”, and also take into account the features of each project.
The requirements under the supervision law may vary depending on which assets (e.g. currencies, goods, real estate or securities) are supported by stablecoin and how the legal rights of its owners will be protected (see the Overview in the Appendix to the Guidelines ICO, Appendix 2).
FINMA provided the legal assessment and indicative classification of the Libra project in accordance with Swiss supervisory law based on the available information. It is worth noting that FINMA focused on the fact that the classification may change during the implementation of the project.
Here are a few key points:
- The project falls under the regulation of Swiss financial market infrastructure. The project, as it is currently envisioned, will require a FINMA payment system license.
- The regulatory requirements for payment systems in Switzerland are based on prevailing international standards, in particular, on the Principles for Financial Market Infrastructures (PFMI). These requirements also apply to cyber risk management.
- The Swiss payment system is automatically covered by the Anti-Money Laundering Act. The highest international anti-money laundering standards must be ensured throughout the project’s ecosystem. Such an ecosystem must be protected from the increased risks of money laundering.
- According to the Financial Market Infrastructure Act (FMIA), all additional services that increase the risks of the payment system must comply with the relevant additional requirements. This means that all potential risks of the Swiss payment system, including banking risks, can be eliminated by introducing the relevant requirements in accordance with the principle of “same risks, same rules”. In connection with the release of Libra payment tokens, the services planned by the Libra project will clearly go beyond a purely payment system and, therefore, will be the subject of such additional requirements.
- These additional requirements will relate in particular to the distribution of capital (for credit, market and operational risks), concentration of risk and liquidity, as well as the management of the Libra reserve.
- Additional requirements will be based on generally accepted standards for similar activities in financial markets and should reflect the scope of the project. For example, for similar banking risks, banking regulatory requirements will apply. Thus, the license of the Swiss payment system will allow you to combine the strengths of banking and infrastructure regulation.
A prerequisite for obtaining a license as a payment system would be that the revenues and risks associated with the management of the reserve are fully covered by the Libra Association, and not by the providers of funds - stablecoin holders.
The planned international scope of the project requires an internationally coordinated approach. In particular, the definition of requirements for reserve management and management, as well as for combating money laundering, should be developed in the framework of international coordination.
Matters beyond supervisory law.
A possible licensing procedure under Swiss supervision legislation will only begin after FINMA receives a specific licensing application. In accordance with its practice, FINMA will not provide public information on the status of any existing licensing procedures and will not speculate on when it may be completed.
Other issues raised in the context of the Libra project, such as those related to tax law, competition law or data protection law, are outside the scope of supervisory law and therefore are not within the competence of FINMA.
In the next message, we will analyze in detail the documents posted below.
Source: FINMA.
CRYPTO-AFFAIR OF THE CENTURY: PLUSTOKEN INVESTORS LOST $ 3 BILLION
Written by Bederov IgorPlusToken crypto wallet, which proposed storing almost all the world's leading cryptocurrencies and making a profit on their investments, can claim the status of the largest fraudulent project in the history of financial pyramids. Users cannot withdraw the equivalent of $ 3 billion from their online wallets.
PlusToken, an international decentralized crypto project of the multi-currency online wallet PlusToken, was launched in April 2018. The project was positioned by the creators as developing a team from South Korea using Samsung technology. The marketing campaign was launched in Asia (China, Japan, South Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam), a number of European countries (Germany and the UK), as well as in Russia.
In addition to the ability to store almost all the world's leading cryptocurrencies in the wallet - Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum, XRP, EOS, IO, Litecoin, Doge and Dash, users were promised a fairly significant return on investment of their cryptocurrency assets - from 6% to 19% per month.
According to experts from Elementus (USA), a company that creates and promotes fintech solutions based on blockchain technology, over 800 thousand Ethereum cryptocurrency depositors have used PlusToken wallets for the entire existence of the project and stored about 10 million ETH on them.
According to the Special elaborations department of the Technopark of St. Petersburg, the PlusToken pyramid attracted about 200 thousand bitcoins, 789 thousand ETH and 26 million EOSIO. All these funds went to wallets controlled by the PlusToken team.
However, interested media write, these estimates are very preliminary, and the amount collected from investors may be much larger. So, experts say, only the Ethereum address of PlusToken stored more than 781,000 ETH, which, in terms of the exchange rate, amounts to more than $ 234 million.
The capitalization of PlusToken at the top of trading reached $ 17 billion. PlusToken was accused of fraud in March 2019, when Chinese police raided PlusToken's offices in Hunan (PRC). The head of PlusToken's Chinese unit, Chen Bo, as well as five other Chinese citizens related to the cryptocurrency wallet project, have disappeared and are on the wanted list.
Problems with the withdrawal of assets from PlusToken wallets began in late June 2019. The Chinese investors were the first to suffer, as evidenced by the entries in the PlusToken support service, which did not respond to calls, and, starting on June 29, the PlusCoin platform token exchange rate remained at the same level ($ 139,237) without hesitation.
On June 29, according to the Dailypost, six Chinese citizens suspected of participating in an Internet scam were arrested on the island of Vanuatu at the request of the Chinese authorities and deported back to China. It is possible, the publication reports that they are precisely the key figures in the PlusToken team.
To date, it is known that the organizers of PlusToken have already managed to cash out part of the bitcoins through crypto exchanges Huobi Global (Singapore) and Bittrex (USA). In particular, the Singapore cryptocurrency exchange got almost half of the funds raised for wallets - about 4.3 million ETH. The other part was transferred to one of the cryptocurrency wallets.
It was possible to track the funds of defrauded investors thanks to the cryptocurrency transaction analysis service created in the Special elaborations department of the Technopark of St. Petersburg.
According to experts, the obvious signs of the financial pyramid of the PlusToken project were tracked from the very beginning. Among them, the referral system of distribution of funds offered to investors, which is characteristic of financial pyramids and MLM marketing, and unjustifiably high monthly profit (from 6% to 19%.). The PlusToken fraudulent scheme is already being compared with the principles of organizing the BitConnect closed cryptocurrency platform. It entered the market through an ICO at the end of December 2016, and by the end of 2017, its BCC tokens have established themselves as one of the fastest growing cryptocurrencies. She guaranteed her investors a 40% return for a month. According to CoinMarketCap, in a fairly short time, BCC capitalization reached $ 2.6 billion, and the ATH rate was $ 460. But in January 2018, BitConnect unexpectedly for its investors announced the closure of the exchange and the lending program, notifying them that they would continue to provide services as a wallet, but at the same time change the format to a media platform. Immediately after this announcement, investors fell into a panic, and the BCC rate lost 96% of the cost.
It is interesting to note that in Russia until now, users have access to the PlusToken mobile wallet, which can be downloaded from the GooglePlay and AppStore stores. For the storage of their crypto assets in the wallet, Russian investors are still guaranteed a profit of 6% to 19% monthly. True, the “blog” section of PlusToken’s Russian site is currently inactive (or deleted), and all consultations are invited to receive via WhatsApp.
Source: IT News.
SPECIAL ELABORATIONS DEPARTMENT AT TECHNOPARK OF ST. PETERSBURG IS PRESENTED FOR INFINITY GROUP
Written by Aleksandr PodobnykhOn September 3, 2019, in St. Petersburg, specialists and residents of the SafeNet RIC of the St. Petersburg Technopark, together with the Russoft NP and Bee Pitron, held a presentation session for the Indian delegation of Infinity Group. The key focus of the event was the creation of a platform for interaction between participants in the Russian-Indian market.
As part of the meeting, Igor Bederov presented the developments of the Special Development Department for a distinguished guest from India. Mr. Darbari drew particular attention to existing developments in the field of cryptocurrency transaction control and crime prevention. According to him, in India, up to 20% of the population and a significant amount of low-level crime use cryptocurrencies. In addition, the country has not resolved the problem of relapse in previously convicted criminals.
Back in July, in the format of the Second Russian-Indian strategic dialogue, in order to establish a technology transfer, an agreement was signed between RUSSOFT and Infinity Group. As a result, the ICT Center of Excellence project was launched in India, designed to establish cooperation between the two countries in the direction of business development and international assistance to SMEs.
The delegation of the Infinity Group, headed by Mr. Darbari, flew to Russia to meet with potential recipients of investments and to transfer technology from Russia to India under the “Made in India” program.

After a tour of the engineering center, SafeNet residents presented their projects in the areas of Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, cyberphysical security, blockchain, virtual and augmented reality. The parties discussed the situation on the international high-tech market and considered options for potential mutually beneficial cooperation. ICT experts emphasized the relevance of Russian solutions to the market of India and other countries and discussed the possibility of implementation.
Source: Engineering center SafeNet.
More...
PLUS TOKEN CRYPTO PYRAMID CLAIMS TO BE THE LARGEST SCAM
Written by Dobryshkin SergeyPlusToken could be the largest scam in the history of financial pyramids. This project has already raised almost $ 3 billion in cryptocurrencies.
At the end of June of this year, six PlusToken project fraud suspects were arrested in China, while another part of the executives is still at large.
According to Elementus researchers, PlusToken collected 10 million ETH from over 800 thousand contributors. In addition to ETH, funds were invested in the project in other digital assets - in bitcoins, XRP and EOS. The total amount of funds raised is impressive - almost $ 3 billion in terms of the exchange rate. Investors live in almost all Asian countries, as well as in Russia, Ukraine, Germany and Canada.
According to preliminary estimates of other researchers, the PlusToken pyramid attracted about 200 thousand bitcoins, 789 thousand ETH and 26 million EOS. All of these funds went to wallets controlled by the PlusToken team. It was possible to track the funds of defrauded investors thanks to the cryptocurrency transaction analysis service created in the Special elaborations department of the Technopark of St. Petersburg. It is known that some of the bitcoins were already cashed by criminals through the Huobi Global and Bittrex crypto exchanges, while the other part settled on one of the crypto wallets.
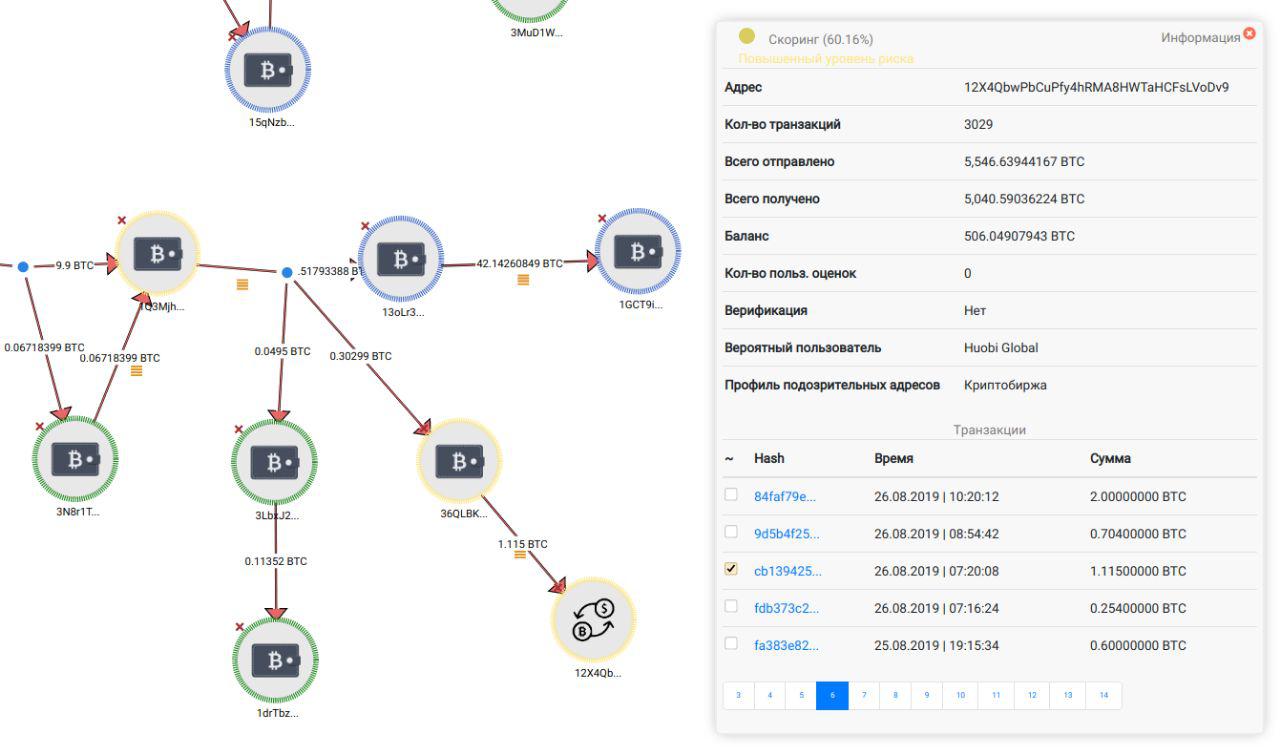
In particular, PlusToken organizers transferred almost half of the funds raised to the Singapore Huobi crypto exchange - at least 4.3 million ETH of the total ETH.
The PlusToken project was launched in 2018 as an international cryptocurrency project and a decentralized solution (crypto wallet), supported by a team from South Korea. Project promotion was supposed mainly in Asian countries - China, Japan, Myanmar, Vietnam, as well as in Russia and Europe. The project immediately had obvious signs of a financial pyramid - a referral system was offered to investors and a monthly profit of 6% to 19% was promised. According to experts, the PlusToken fraudulent scheme is organized on the principle of the already closed BitConnect platform - with tokens and dividends. The capitalization of BitConnect tokens at the top of trading was a little over $ 121 million, and the capitalization of PlusToken was already $ 17 billion.
Although the PlusToken pyramid has ceased to exist, "a holy place does not exist empty." Similar projects Cloud Token and VDS (Vollar) appear on the market with a market capitalization of $ 1 billion and are already becoming popular, including among Russian-speaking users.
Earlier we reported what a financial pyramid is. Often, pyramids are often understood as MLM - a method of marketing promotion and sales that has been used for many years. Nevertheless, there are different nuances. A synonym for the “evil” pyramid is a scheme named after Ponzi, an Italian-American scammer who created a scam, massively promising investors profit from the contributions of new participants, forming a pyramid until the collapse that inevitably occurs, according to the nature of speculation and any financial bubbles. In our country, Mavrodi distinguished himself with such a fraud with the MMM pyramid. The concept of a financial pyramid is fixed at the legislative level and you can pay for it, including imprisonment for up to six years. So far, the practice of applying this criminal article is not very common.
The Central Bank of Russia gives several main signs of the financial pyramid in its recommendations: paying money to participants from funds contributed by other participants, lack of licenses for this type of activity, promise of high profitability, lack of information about the financial position of the organization, lack of own fixed assets or assets, lack of certain type of activity of the company.
Source: CryptoRussia.ru
GUIDANCE FOR A RISK-BASED APPROACH TO VIRTUAL ASSETS AND VIRTUAL ASSET SERVICE PROVIDERS
Written by Aleksandr PodobnykhOrlando, FL, United States – 21 June 2019. Financial innovation has drastically changed the financial landscape. New technologies, services and products offer efficient alternatives to classic financial products and can improve financial inclusion. At the same time, the speed and anonymity of some of these innovative products can attract criminals and terrorist who wish to use them to launder the proceeds of their crimes and finance their illicit activities.
This guidance will help countries and virtual asset service providers understand their anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing obligations, and effectively implement the FATF’s requirements as they apply to this sector.
This guidance follows revisions to the FATF Recommendations in October 2018 and June 2019 in response to the increasing use of virtual assets for money laundering and terrorist financing. The FATF strengthened its standards to clarify the application of anti-money laundering and counter- terrorist financing requirements on virtual assets and virtual asset service providers. Countries are now required to assess and mitigate their risks associated with virtual asset financial activities and providers; license or register providers and subject them to supervision or monitoring by competent national authorities. Virtual asset service providers are subject to the same relevant FATF measures that apply to financial institutions.
The guidance addresses the following:
- How do virtual assets activities and virtual asset service providers fall within the scope of the FATF Recommendations? (Section II)
- How should countries and competent authorities apply the FATF Recommendations in the context of virtual assets or virtual asset service providers? (Section III)
- How do the FATF Recommendations apply to virtual asset service providers, and other entities (including banks, securities broker-dealers) that engage in or provide virtual asset covered activities?
The guidance, which benefited from dialogue with the private sector, also includes examples of national approaches to regulating and supervising virtual asset activities and virtual asset service providers to prevent their misuse for money laundering and terrorist financing.
Source: Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
CYBERPOL PUBLIC SEARCH CRIMINAL DATABASE TO INCLUDE CRYPTOCURRENCY WALLETS USED IN CYBERCRIME
Written by Aleksandr PodobnykhBRUSSELS, 1000, BELGIUM, June 18, 2019. CYBERPOL Public Search Criminal Database to include Crypto Currency wallets used in cyber crime.
CYBERPOL The International Cyber Policing Organization established by decree no WL 22/16.595 established today four years ago in Brussels made available to the public the first cyber criminal database empowered by the "Neural symbiotic network of the super computer" as the international cyber utility agency leader in investigation in cyber crimes and terror of the Dark-Web today.
This first Cyber Criminal Public Record Database in Beta Test mode currently will allow four basic levels of searching of wanted cyber criminals allowing for verification and searches of IP's, emails and Cryptocurrency wallets used in on-line scams related to cyber crimes listed in the database.
In addition to this, all cryptowallets using crypto currencies in cybercrime will now be listed on the Cyber Crime search engine by CYBERPOL organization making it very difficult for cyber criminals to use crypto-currencies as payment methods for scams and cyber crimes.
You can now report any scam email to CYBERPOL that when verified will be listed in the CYBERPOL Cyber Criminal Public Database open to public to search.
More than £108,000 in bitcoin was paid by victims of the WannaCry ransomware attacks using bitcoin as undetectable crypto-currency payment. Since such wallets used in crimes are not considered privacy breaches but in the interest of the law it is in the public interest to warn public and make such wallets black listed public records globally before further victims falls pray to cyber crimes Baretzky President of CYBERPOL said.
Public and law enforcement can use this CYBERPOL facilities for free and report such e-mail of extortion to be entered into the public records of CYBERPOL Public Utility directly by requests.
Several entries is already public to search on-line and don't try to fool CYBERPOL. The tracking of cyber crimes goes the extra mile to track the same hackers when visiting the search engine on CYBERPOL website using a new AI (Artificial Intelligence) named 666 to capture both mac and serial number of such computers. Don't be a hackers fool to search yourselves if you are already involved in cyber crimes, the CYBERPOL Spokes Person warned.
This will be a huge blow for crypto currencies and wallets used in cyber crimes and scams as the wallet numbers will be public listed and open to see to all public and law-enforcement free of charges in disrupting cyber crimes.
The message is clear and simple President Ricardo Baretzky of CYBERPOL said "Don't use any Crypto Currencies in INTERNET crimes as we will not only find you but list your crypto WALLET accounts for good in the block-chain based search engine of CYBERPOL Supper Computer AI 666 symbiotic neural network and let me assure all those financial criminals, once listed there is no escape! I hope this message is clear to criminals and corruption".
It seems the days messing with elections using secret corruption payments could be counted as CYBERPOL has set a new paradigm in combating cyber crimes and global corruption never seen before...
Source: EIN Presswire.
ANNOUNCED THE CREATION OF A SPECIAL ELABORATIONS DEPARTMENT
Written by Aleksandr PodobnykhIn early July, SafeNet regional engineering center (structural division of JSC Technopark of St. Petersburg) has introduced a new project.
Thus, together with the company Internet-Rozysk was announced the creation of the Special elaborations department. Which purpose is the organization of work with information and analytical and other products intended for the prevention, suppression and investigation of the offenses committed by means of information and telecommunication technologies.
Key activities of the new Department:
1. interaction with profile startups, companies and developers;
2. organization of interaction with state and law enforcement agencies. Control over the legality and legality of the development;
3. consulting and carrying out examinations, development of methodical and scientific base, training and professional development for the persons engaged in law enforcement activity, and also other persons;
4. organization of demonstration zones, exhibitions, interaction with the media, negotiations aimed at attracting interest in the development of the Department, the implementation of its product line, promotion of activities.
Developers engaged in the following project categories are invited to interact:
- assessment of reliability of contractors and staff;
- non-instrumental lie detection;
- detection of illegal activities in social networks;
- analysis and tracking of cryptocurrency transactions;
- establishing users phone numbers and email addresses;
- establishing users of secure messengers;
- enrichment and analysis of large amounts of publicly available data;
- detection and suppression of confidential information leaks;
- darknet Analytics;
- analysis and decoding of Internet traffic.
Source: SafeNet еngineering center.
О КОСАтка
Корпоративная система аналитики Транзакция Криптовалюта Актив - кибербезопасность инфраструктуры блокчейнов и антифрод в криптовалютной сфере (антискам, прозрачность, комплаенс).
Связаться
Российская Федерация, Москва
Тел.: +7 (911) 999 9868
Факс:
Почта: cosatca@ueba.su
Сайт: www.ueba.su














